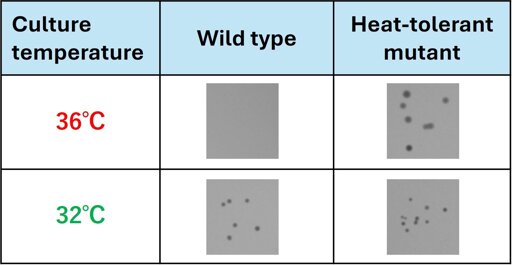
Heat-resilient biofertilizers could help crops cope with rising temperatures but engineering them has been slow and uncertain. A new study at the National Institutes for Quantum Science and Technology (QST) shows that pairing experimental evolution with controlled gamma-ray mutagenesis can accelerate the path to heat-tolerant nitrogen-fixing bacteria, shortening development timelines and opening practical routes to more reliable, climate-ready microbial products for agriculture, food processing, pharmaceuticals, and biofuel production.
From Biology News - Evolution, Cell theory, Gene theory, Microbiology, Biotechnology via This RSS Feed.
You must log in or # to comment.